Dataset
Attribute Information:
1. sepal length in cm
2. sepal width in cm
3. petal length in cm
4. petal width in cm
5. class:
-- Iris Setosa
-- Iris Versicolour
-- Iris Virginica
Table preparation
create database iris;
use iris;
create external table raw (
sepal_length int,
sepal_width int,
petal_length int,
petak_width int,
class string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
STORED AS TEXTFILE LOCATION '/dataset/iris/raw';
$ sed '/^$/d' iris.data | hadoop fs -put - /dataset/iris/raw/iris.data
create table label_mapping
as
select
class,
rank - 1 as label
from (
select
distinct class,
dense_rank() over (order by class) as rank
from
raw
) t
;
create table training
as
select
rowid() as rowid,
array(t1.sepal_length, t1.sepal_width, t1.petal_length, t1.petak_width) as features,
t2.label
from
raw t1
JOIN label_mapping t2 ON (t1.class = t2.class)
;
Training
train_randomforest_classifier takes a dense features in double[] and a label starting from 0.
CREATE TABLE model
STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE
AS
select
train_randomforest_classifier(features, label)
-- v0.5.0 and later
-- train_randomforest_classifier(features, label) as (model_id, model_weight, model, var_importance, oob_errors, oob_tests)
-- v0.4.1-alpha.2 and before
-- train_randomforest_classifier(features, label) as (pred_model, var_importance, oob_errors, oob_tests)
-- from v0.4.1 to v0.4.2-rc4
-- train_randomforest_classifier(features, label) as (model_id, model_type, pred_model, var_importance, oob_errors, oob_tests)
from
training;
Caution
Note that model storage format is different between versions as seen the above.
hive> desc extended model;
| col_name | data_type |
|---|---|
| model_id | string |
| model_weight | double |
| model | string |
| var_importance | array |
| oob_errors | int |
| oob_tests | int |
Training options
-help option shows usage of the function.
select train_randomforest_classifier(features, label, "-help") from training;
> FAILED: UDFArgumentException
usage: train_randomforest_classifier(array<double|string> features, int
label [, const array<double> classWeights, const string options]) -
Returns a relation consists of <int model_id, int model_type,
string pred_model, array<double> var_importance, int oob_errors,
int oob_tests, double weight> [-attrs <arg>] [-depth <arg>] [-help]
[-leafs <arg>] [-min_samples_leaf <arg>] [-rule <arg>] [-seed
<arg>] [-splits <arg>] [-stratified] [-subsample <arg>] [-trees
<arg>] [-vars <arg>]
-attrs,--attribute_types <arg> Comma separated attribute types (Q
for quantitative variable and C for
categorical variable. e.g.,
[Q,C,Q,C])
-depth,--max_depth <arg> The maximum number of the tree depth
[default: Integer.MAX_VALUE]
-help Show function help
-leafs,--max_leaf_nodes <arg> The maximum number of leaf nodes
[default: Integer.MAX_VALUE]
-min_samples_leaf <arg> The minimum number of samples in a
leaf node [default: 1]
-rule,--split_rule <arg> Split algorithm [default: GINI,
ENTROPY]
-seed <arg> seed value in long [default: -1
(random)]
-splits,--min_split <arg> A node that has greater than or
equals to `min_split` examples will
split [default: 2]
-stratified,--stratified_sampling Enable Stratified sampling for
unbalanced data
-subsample <arg> Sampling rate in range (0.0,1.0]
-trees,--num_trees <arg> The number of trees for each task
[default: 50]
-vars,--num_variables <arg> The number of random selected
features [default:
ceil(sqrt(x[0].length))].
int(num_variables * x[0].length) is
considered if num_variable is (0,1]
Caution
-num_trees controls the number of trees for each task, not the total number of trees.
Parallelize Training
To parallelize RandomForest training, you can use UNION ALL as follows:
CREATE TABLE model
STORED AS ORC tblproperties("orc.compress"="SNAPPY")
-- STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE
AS
select
train_randomforest_classifier(features, label, '-trees 25')
from
training
UNION ALL
select
train_randomforest_classifier(features, label, '-trees 25')
from
training
;
Learning stats
Variable importance and Out Of Bag (OOB) error rate of RandomForest can be shown as follows:
select
array_sum(var_importance) as var_importance,
sum(oob_errors) / sum(oob_tests) as oob_err_rate
from
model;
[6.837674865013268,4.1317115752776665,24.331571871930226,25.677497925673062] 0.056666666666666664
Prediction
-- set hivevar:classification=true;
set hive.auto.convert.join=true;
set hive.mapjoin.optimized.hashtable=false;
create table predicted
as
SELECT
rowid,
-- rf_ensemble(predicted) as predicted
-- v0.5.0 or later
rf_ensemble(predicted.value, predicted.posteriori, model_weight) as predicted
-- rf_ensemble(predicted.value, predicted.posteriori) as predicted -- avoid OOB accuracy (i.e., model_weight)
FROM (
SELECT
rowid,
-- from v0.4.1 to v0.4.2-rc4
-- tree_predict(p.model_id, p.model_type, p.pred_model, t.features, ${classification}) as predicted
-- v0.5.0 or later
p.model_weight,
tree_predict(p.model_id, p.model, t.features, "-classification") as predicted
-- tree_predict(p.model_id, p.model, t.features, ${classification}) as predicted
-- tree_predict_v1(p.model_id, p.model_type, p.pred_model, t.features, ${classification}) as predicted -- to use the old model in v0.5.0 or later
FROM
model p
LEFT OUTER JOIN -- CROSS JOIN
training t
) t1
group by
rowid
;
Note
Left outer join without a join condition (i.e., model p LEFT OUTER JOIN training t) is a trick to fix the left table for cross join.
Caution
tree_predict_v1 is for the backward compatibility for using prediction models built before v0.5 on v0.5 or later.
Parallelize Prediction
The following query runs predictions in N-parallel. It would reduce elapsed time for prediction almost by N.
SET hivevar:classification=true;
set hive.auto.convert.join=true;
SET hive.mapjoin.optimized.hashtable=false;
SET mapred.reduce.tasks=8;
drop table predicted;
create table predicted
as
SELECT
rowid,
-- rf_ensemble(predicted) as predicted
-- v0.5.0 or later
rf_ensemble(predicted.value, predicted.posteriori, model_weight) as predicted
-- rf_ensemble(predicted.value, predicted.posteriori) as predicted -- avoid OOB accuracy (i.e., model_weight)
FROM (
SELECT
t.rowid,
-- from v0.4.1 to v0.4.2-rc4
-- tree_predict(p.model_id, p.model_type, p.pred_model, t.features, ${classification}) as predicted
-- v0.5.0 or later
p.model_weight,
tree_predict(p.model_id, p.model, t.features, "-classification") as predicted
-- tree_predict(p.model_id, p.model, t.features, ${classification}) as predicted
-- tree_predict_v1(p.model_id, p.model_type, p.pred_model, t.features, ${classification}) as predicted as predicted -- to use the old model in v0.5.0 or later
FROM (
SELECT
-- from v0.4.1 to v0.4.2-rc4
-- model_id, model_type, pred_model
-- v0.5.0 or later
model_id, model_weight, model
FROM model
DISTRIBUTE BY rand(1)
) p
LEFT OUTER JOIN training t
) t1
group by
rowid;
Evaluation
select count(1) from training;
150
set hivevar:total_cnt=150;
WITH t1 as (
SELECT
t.rowid,
t.label as actual,
p.predicted.label as predicted
FROM
predicted p
LEFT OUTER JOIN training t ON (t.rowid = p.rowid)
)
SELECT
count(1) / ${total_cnt}
FROM
t1
WHERE
actual = predicted
;
0.98
Graphviz export
Note
tree_export feature is supported from Hivemall v0.5.0 or later.
Better to limit tree depth on training by -depth option to plot a Decision Tree.
Hivemall provide tree_export to export a decision tree into Graphviz or human-readable Javascript format. You can find the usage by issuing the following query:
> select tree_export("","-help");
usage: tree_export(string model, const string options, optional
array<string> featureNames=null, optional array<string>
classNames=null) - exports a Decision Tree model as javascript/dot]
[-help] [-output_name <arg>] [-r] [-t <arg>]
-help Show function help
-output_name,--outputName <arg> output name [default: predicted]
-r,--regression Is regression tree or not
-t,--type <arg> Type of output [default: js,
javascript/js, graphviz/dot
CREATE TABLE model_exported
STORED AS ORC tblproperties("orc.compress"="SNAPPY")
AS
select
model_id,
tree_export(model, "-type javascript", array('sepal_length','sepal_width','petal_length','petak_width'), array('Setosa','Versicolour','Virginica')) as js,
tree_export(model, "-type graphviz", array('sepal_length','sepal_width','petal_length','petak_width'), array('Setosa','Versicolour','Virginica')) as dot
from
model
-- limit 1
;
digraph Tree {
node [shape=box, style="filled, rounded", color="black", fontname=helvetica];
edge [fontname=helvetica];
0 [label=<petal_length ≤ 2.599999964237213>, fillcolor="#00000000"];
1 [label=<predicted = Setosa>, fillcolor="0.0000,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
0 -> 1 [labeldistance=2.5, labelangle=45, headlabel="True"];
2 [label=<petal_length ≤ 4.950000047683716>, fillcolor="#00000000"];
0 -> 2 [labeldistance=2.5, labelangle=-45, headlabel="False"];
3 [label=<petak_width ≤ 1.6500000357627869>, fillcolor="#00000000"];
2 -> 3;
4 [label=<predicted = Versicolour>, fillcolor="0.3333,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
3 -> 4;
5 [label=<sepal_width ≤ 3.100000023841858>, fillcolor="#00000000"];
3 -> 5;
6 [label=<predicted = Virginica>, fillcolor="0.6667,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
5 -> 6;
7 [label=<predicted = Versicolour>, fillcolor="0.3333,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
5 -> 7;
8 [label=<petak_width ≤ 1.75>, fillcolor="#00000000"];
2 -> 8;
9 [label=<petal_length ≤ 5.299999952316284>, fillcolor="#00000000"];
8 -> 9;
10 [label=<predicted = Versicolour>, fillcolor="0.3333,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
9 -> 10;
11 [label=<predicted = Virginica>, fillcolor="0.6667,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
9 -> 11;
12 [label=<predicted = Virginica>, fillcolor="0.6667,1.000,1.000", shape=ellipse];
8 -> 12;
}
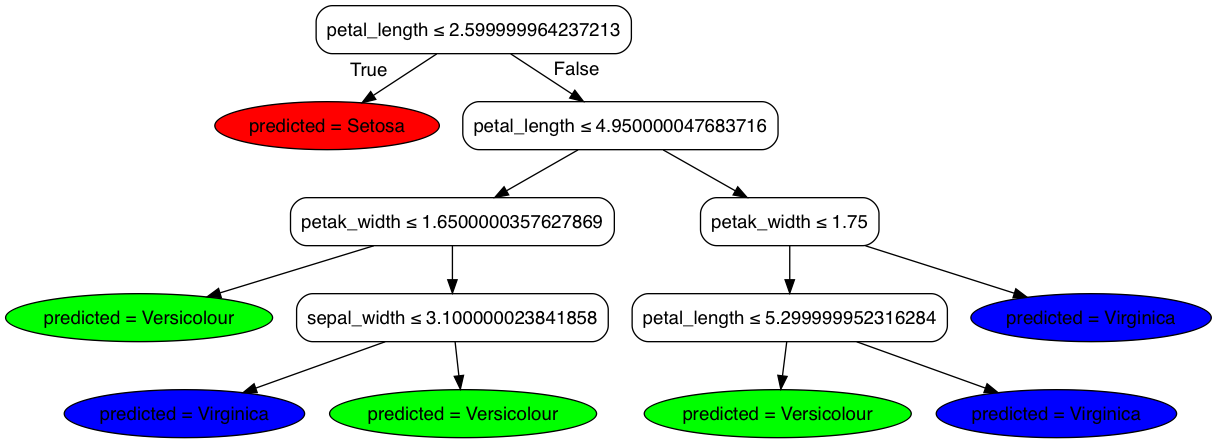
You can draw a graph by dot -Tpng iris.dot -o iris.png or using Viz.js.